
SAN storage can be a network of multiple devices of various types, including SSD and flash storage, hybrid storage, hybrid cloud storage, backup software and appliances, and cloud storage. NAS is often a single device made up of redundant storage containers or a redundant array of independent disks (RAID). Two common network-based storage setups are network-attached storage (NAS) and storage area network (SAN). Its off-site storage capability also makes it better suited for backups and data protection. Network-based storage allows more than one computer to access it through a network, making it better for data sharing and collaboration. DAS devices include floppy disks, optical discs-compact discs (CDs) and digital video discs (DVDs)-hard disk drives (HDD), flash drives and solid-state drives (SSD). DAS can provide decent local backup services, too, but sharing is limited. Often, it's the only machine connected to it. This storage is often in the immediate area and directly connected to the computing machine accessing it. Data storage devices come in two main categories: direct area storage and network-based storage.ĭirect area storage, also known as direct-attached storage (DAS), is as the name implies. To store data, regardless of form, users need storage devices. However, at a fundamental level, there are two foundations to data storage: the form in which data takes and the devices data is recorded and stored on.

Users instruct computers to access data from and store data to these storage devices. In simple terms, modern computers, or terminals, connect to storage devices either directly or through a network. So, to avoid data loss, organizations can also employ data storage as backup solutions. And the other side of requiring huge data storage amounts is protecting against data loss due to disaster, failure or fraud. Today, organizations and users require data storage to meet today's high-level computational needs like big data projects, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning and the internet of things (IoT). Users can also share data storage with others. Computers can read input data from various sources as needed, and it can then create and save the output to the same sources or other storage locations.
And instead of manually entering data into a computer, users can instruct the computer to pull data from storage devices. And should the computer power down, the data is retained. With data storage space, users can save data onto a device. When a computer powers down, so does the RAM's ability to retain data. They control a computer's basic functionality.Īlthough advances have been made in computer memory with dynamic RAM (DRAM) and synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), they are still limited by cost, space and memory retention. Read-only memory (ROM) is, as the name suggests, the data can only be read but not necessarily edited. But its storage capacity and memory retention are limited. One short-term solution is computer memory, also known as random access memory (RAM). However, they have found early on in the computer-era that continually entering data manually is time- and energy-prohibitive. Users can enter the input data directly into a computer. But a computer's CPU can't compute anything or produce output data without the user's input.

There are two types of digital information: input and output data.


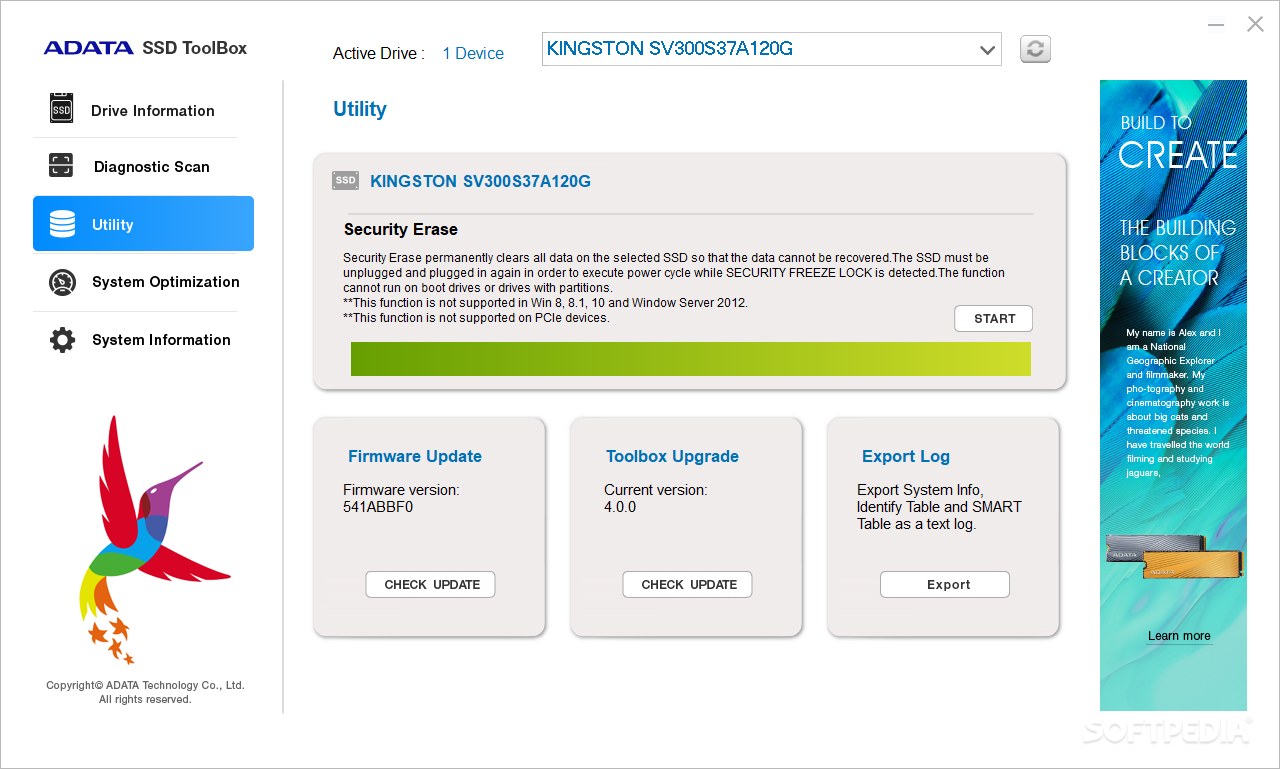
 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
